When considering excavation methods for your project, one question that often arises is, “Is directional drilling right for my project?” In this extensive guide, we’ll explore the realm of horizontal directional drilling (HDD) to assess its compatibility with different projects. By exploring the benefits, applications, and considerations of directional drilling, you’ll gain insights to determine if it’s the right choice for your project needs.
What is Horizontal Directional Drilling?
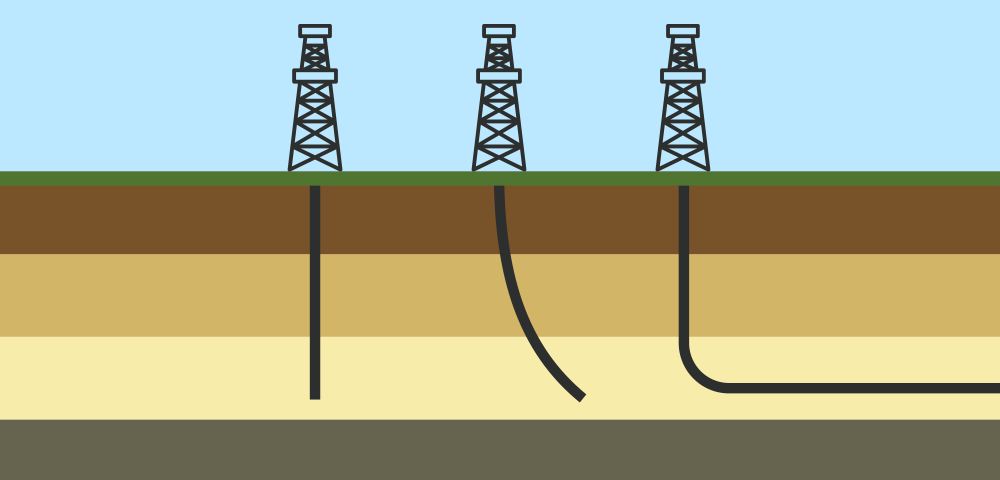
Horizontal directional drilling (HDD) is a trenchless method used to install underground utilities, such as pipelines, conduits, and cables, without the need for traditional open-cut excavation. This technique involves drilling a borehole underground and then steering the drill horizontally to create a pathway for the utility installation.
Benefits of Horizontal Directional Drilling:
- Minimal Surface Disturbance: HDD minimizes disruption to the surface environment since excavation is conducted underground, reducing the need for disruptive trenching and excavation work.
- Preservation of Landscapes: By avoiding extensive excavation, HDD helps preserve landscapes, vegetation, and structures, making it suitable for environmentally sensitive areas and urban settings.
- Reduced Environmental Impact: HDD reduces the risk of environmental contamination and disturbance by minimizing soil erosion, habitat disruption, and the release of pollutants.
- Cost Savings: Although initial setup costs may be higher than traditional excavation methods, HDD can result in long-term cost savings by reducing restoration expenses and project delays.
Applications of Horizontal Directional Drilling:
- Utility Installations: HDD is commonly used for installing pipelines, telecommunications cables, electrical conduits, and sewer lines beneath roads, railways, rivers, and environmentally sensitive areas.
- Crossings: HDD is ideal for creating crossings beneath obstacles such as rivers, highways, railways, and environmentally protected areas where traditional excavation methods are impractical or prohibited.
- Infrastructure Projects: HDD plays a crucial role in infrastructure projects such as water distribution, wastewater management, gas distribution, and broadband connectivity, where underground utilities need to be installed with minimal disruption.
Considerations for Horizontal Directional Drilling:
- Subsurface Conditions: Assess subsurface conditions, including soil type, rock formations, groundwater levels, and potential obstacles, to determine the feasibility and challenges of directional drilling.
- Regulatory Requirements: Familiarize yourself with local regulations, permits, and environmental guidelines governing directional drilling to ensure compliance and mitigate risks.
- Project Scale: Evaluate the scale and complexity of your project to determine if HDD is suitable in terms of equipment capabilities, project timelines, and budgetary constraints.
Conclusion:
Horizontal directional drilling offers numerous benefits and applications for a wide range of projects requiring underground utility installations. By understanding the advantages, applications, and considerations of directional drilling, you can assess if it’s the right choice for your project needs. Whether it’s minimizing surface disturbance, preserving landscapes, or reducing environmental impact, HDD provides a versatile and efficient solution for underground infrastructure projects.